
- Arithmetic subtest stronger than digit span serial#
- Arithmetic subtest stronger than digit span trial#
These results suggest that although Arithmetic may be considered a measure of concentration or working memory, many other factors influence it and its specificity as a concentration measure is limited. Digit Span Backward no longer has a three-digit sample trial: all sample trials are two digits in length. In short, Night Before Sleep was shown to have a significant effect on Digit Symbol performance. Smokers performed worse than non-smokers in tests of arithmetic and digit span forward (t 4.25, 2.05, both P <.
Arithmetic subtest stronger than digit span trial#
Rhyming digits within a single trial were eliminated wherever possible, so these observations may be more useful than on prior editions. average than Males in all three subtests performances. For the Forward task, the individual repeats numbers spoken by the examiner. Digit Span includes three tasks: Forward, Backward, and Sequencing. LetterNumber Sequencing (LN) serves as a supplemental subtest for individuals aged 1669 years. Measures of anxiety and of background factors, such as perceived difficulty learning Arithmetic, were weakly related to Arithmetic scores. WAIS-III users will note a number of changes to this subtest. The core Working Memory subtests are Digit Span (DS) and Arithmetic (AR). Moderate contributions to Arithmetic performance were found for most other cognitive measures. Arithmetic also showed a high association with Arithmetic skill and verbal memory. The addition of the Symbol Search subtest did not strengthen the. Digit span was tested using the WISC-R digit span subtest (Wechsler, 1986). Digit Span will also not consistently align itself with a particular composite. The results indicate a strong association between WAIS-III Arithmetic and the other WMI (Working Memory Index) subtests. memory span is a better predictor of arithmetic ability than processing speed. or Spanish-speaking children more consistently report that children with math difficulties perform worse on digit span backward than same-aged peers (D. Participants were 118 adults referred for neuropsychological assessment. The current study was intended to examine these to further characterize what is measured by the Arithmetic subtest. However, a wide range of other influences on Arithmetic performance has been proposed. These results support previous findings identifying differences between the Digit Span subtests and the utility of examining traditional scoring procedures.ĭigit Span complex span tasks neuropsychological assessment partial scoring working memory.In the Wechsler system the Arithmetic subtest has been viewed as a measure of concentration, working memory, or freedom from distractibility. The results showed that when differences were found, partial scoring was associated with stronger relationships with Digit Span Backwards but weaker relationships with Digit Span Forward and Sequencing compared with traditional scoring. The current study compared the traditional all-or-nothing scoring method and the partial scoring method on Digit Span with other working memory measures and with measures of general fluid intelligence. These subtest scores range from 1 to 19, with scores between 8 and 12 typically considered average.
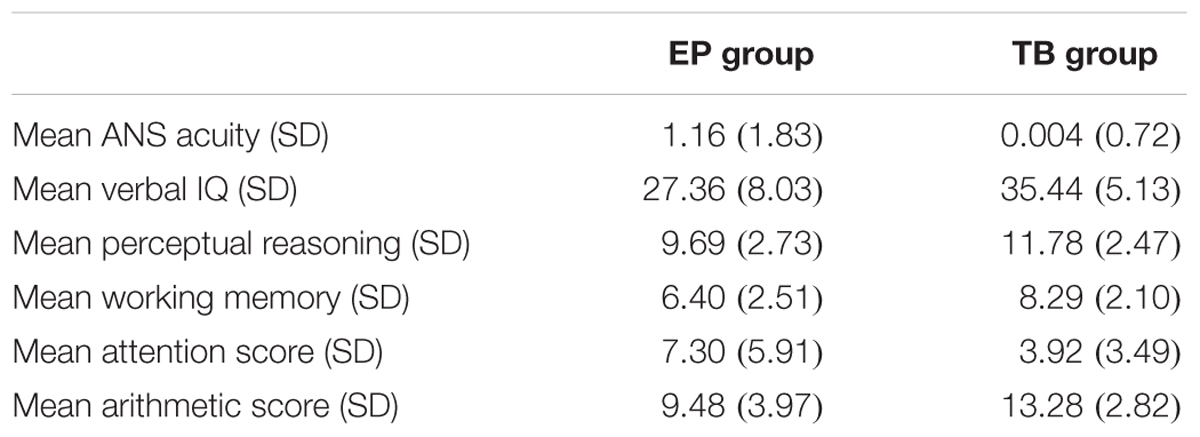

The primary and secondary subtests are on a scaled score metric with a mean of 10 and a standard deviation (SD) of 3.
Arithmetic subtest stronger than digit span serial#
Partial scoring involves awarding credit for all digits recalled in the correct serial location, whereas traditional scoring involves only awarding credit for a trial if all digits are recalled in the correct serial location. assessing the intelligence of children ages 6:0-16:11. However, when using standardized scoring procedures, previous studies have demonstrated inconsistent relationships between Digit Span subtests and working memory measures frequently used in cognitive psychology experiments. The Digit Span test is a widely used working memory measure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
